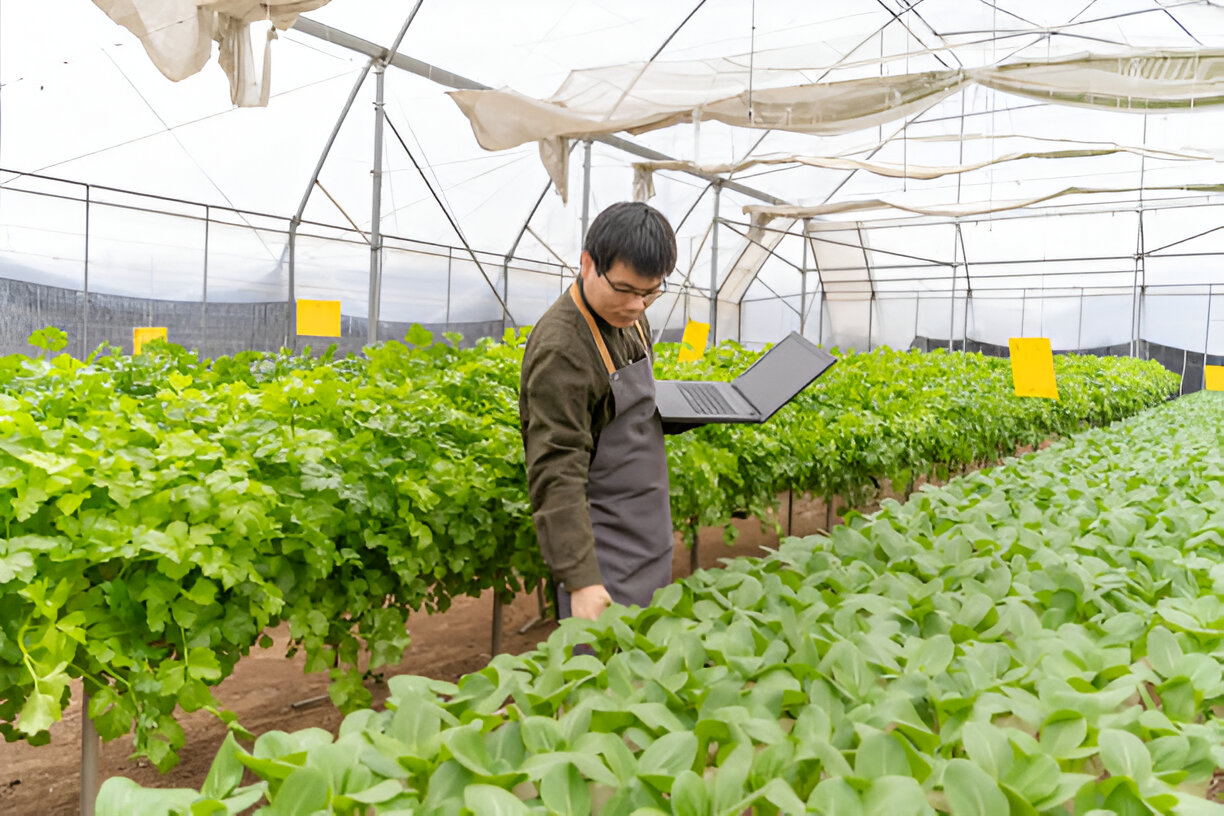
As Malaysia advances towards a more sustainable future, the green economy is gaining momentum. Green jobs, which focus on environmental protection, sustainable practices, and renewable energy, are increasingly becoming integral to the country’s economic landscape. This article explores the burgeoning green job market in Malaysia, highlighting opportunities in sustainable industries and environmental protection.
1. Overview of the Green Economy in Malaysia
Government Initiatives:
- Policy Framework: The Malaysian government has set ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable development through various policies and frameworks, such as the Malaysia Green Technology Master Plan and the National Policy on Climate Change.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Malaysia is committed to achieving the United Nations’ SDGs, particularly those related to clean energy, sustainable cities, and climate action.
Economic Drivers:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Efforts to combat climate change are driving investments in green technologies and sustainable practices.
- Renewable Energy Transition: The push towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power is creating new job opportunities in the green sector.
2. Green Job Opportunities
1. Renewable Energy
- Solar Energy Technician: Installation, maintenance, and repair of solar panels and systems.
- Wind Turbine Technician: Maintenance and troubleshooting of wind turbines and associated equipment.
- Energy Consultant: Advising businesses and government agencies on energy efficiency and renewable energy solutions.
Notes:
- Growing Demand: The expansion of renewable energy projects, including solar farms and wind installations, is creating a growing demand for skilled professionals in the renewable energy sector.
2. Environmental Protection
- Environmental Scientist: Conducting research and analysis to assess environmental impacts and develop strategies for protection.
- Conservation Officer: Working on conservation projects to protect natural habitats and biodiversity.
- Waste Management Specialist: Developing and implementing waste reduction and recycling programs.
Notes:
- Diverse Roles: Opportunities in environmental protection range from scientific research to hands-on conservation work, reflecting the broad scope of the field.
3. Sustainable Agriculture
- Agroecologist: Studying and implementing sustainable agricultural practices to improve crop yields and environmental health.
- Organic Farming Specialist: Managing organic farms and promoting practices that minimize environmental impact.
- Sustainability Consultant: Advising agricultural businesses on sustainable practices and resource management.
Notes:
- Food Security and Sustainability: The focus on sustainable agriculture supports food security while minimizing environmental impact.
4. Green Building and Construction
- Green Building Architect: Designing energy-efficient and environmentally friendly buildings and structures.
- Sustainable Construction Manager: Overseeing construction projects with a focus on sustainable practices and materials.
- Energy Efficiency Auditor: Assessing building energy use and recommending improvements to enhance efficiency.
Notes:
- Building Sector Shift: The adoption of green building standards and sustainable construction methods is transforming the construction industry.
5. Water Management
- Water Resource Engineer: Designing and managing systems for efficient water use and conservation.
- Hydrologist: Studying water cycles and developing strategies for sustainable water management.
- Wastewater Treatment Specialist: Managing and improving processes for treating and recycling wastewater.
Notes:
- Critical Resource Management: Effective water management is essential for sustainability and resilience in both urban and rural areas.
3. Skills and Qualifications for Green Jobs
Educational Requirements:
- Relevant Degrees: Degrees in environmental science, renewable energy, engineering, or related fields are often required for technical green jobs.
- Certifications: Professional certifications in areas like solar technology, environmental management, and energy efficiency can enhance job prospects.
Skills Needed:
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in relevant technologies and methodologies, such as renewable energy systems or environmental monitoring tools.
- Analytical Skills: Ability to analyze data, assess environmental impacts, and develop effective solutions.
- Communication Skills: Strong communication skills for working with stakeholders, educating the public, and promoting sustainable practices.
4. Future Outlook and Trends
Expanding Green Sectors:
- Green Finance: Growth in green bonds and investment in sustainable projects is creating opportunities in green finance and investment advisory roles.
- Circular Economy: The shift towards a circular economy, focusing on reducing waste and reusing materials, is opening new career paths in recycling and resource management.
Government Support:
- Incentives and Programs: Government incentives, such as subsidies for renewable energy projects and funding for environmental research, are likely to boost green job creation.
- Public Awareness: Increased public awareness of environmental issues is driving demand for green products and services, further supporting job growth in the sector.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Skill Gap:
- Training Needs: There may be a gap between the skills required for green jobs and those possessed by the current workforce, necessitating targeted training and educational programs.
Industry Adoption:
- Sector-Specific Challenges: Different sectors may face unique challenges in adopting green practices, requiring tailored approaches to job creation and skills development.
Economic Factors:
- Funding and Investment: The growth of green jobs depends on continued investment and funding in sustainable projects and technologies.
The green economy in Malaysia is expanding rapidly, offering a range of opportunities in sustainable industries and environmental protection. From renewable energy and environmental protection to sustainable agriculture and green building, the demand for green jobs is set to grow as Malaysia continues its journey towards a more sustainable future. By staying informed about emerging trends, required skills, and available opportunities, individuals and businesses can contribute to and benefit from the growth of Malaysia’s green economy.